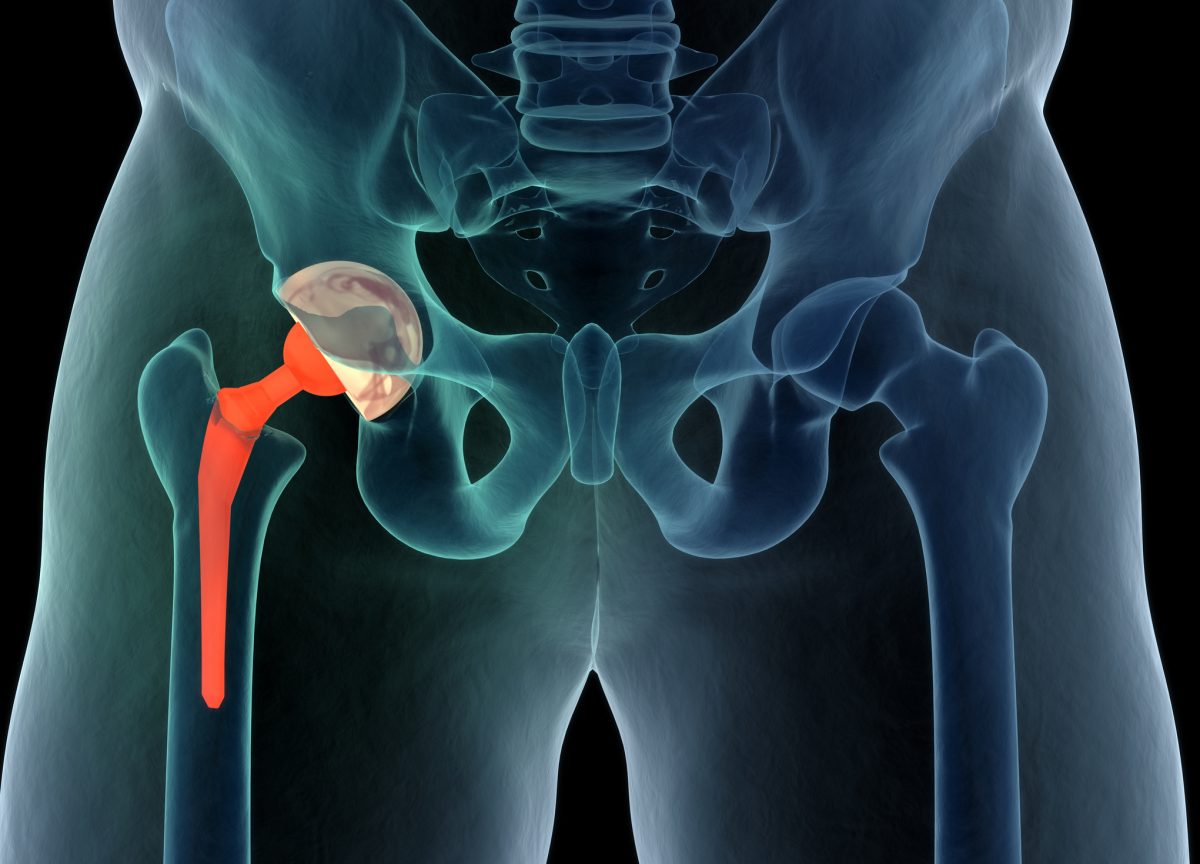
Orthopedic injuries damage the musculoskeletal system. Common orthopedic injuries are shoulder injuries and hip dislocations. The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint; therefore, it can withstand repeated rotation. Smooth gliding of the joint is necessary for seamless mobility. Cartilage tissue in the hip bone is sturdy. However, with age and use, it can wear down. State-of-the-art technology at the Katy total hip replacement center in Texas, leverages on regenerative properties of cartilage tissue to heal and repair worn-out hip joints.
Causes of Hip Injury
Inflamed Tendons
Too many strenuous activities adversely affect your tendons. Prolonged stress on the tendons forces them to crumble and rupture from muscle sinews. Chronic inflammation may develop into a permanent hip injury.
Arthritis
This is the most common cause of long-term pain. Severe stages of arthritis cause excruciating pain and may immobilize you if not treated early. Age-related osteoarthritis is more prevalent in the world than rheumatoid arthritis and is the primary cause of arthritis-associated hip injuries.
Hip Fractures
The sudden shift of the hip bone tears ligaments in the joint. Accidents and lousy walking and sitting posture cause hip fractures. The elderly population is more prone to hip fractures due to a weakening skeletal system.
Hip Treatment Options:
- Hip Prosthesis
A surgeon removes the worn-out joint with a prosthetic in this treatment option. The procedure is done under general anesthesia or intravenous sedation. Ultrasound scanning and an x-ray are done on the injured ligament by a radiologist. Imaging results provide a detailed view of the cartilage to determine where incisions are made. The surgeon will make incisions depending on the extent of the damage. The physician may insert a drain to drain excess fluid from the joint before preparing the head part of the prosthetic. The surgeon will then screw the implants to your leg with little play to enhance flexibility. Prosthetics mimic the movement of natural hip joints to restore mobility. Most prosthetics are durable; however, the longevity of the shafts is contingent on the post-surgery lifestyle. Carry out your normal activities with minimal physical impact on your thighs.
- Physiotherapy
Mild hip injuries do not necessarily need surgery. Physiotherapy uses massage, a program of specific exercises, and pain-relieving medication to manage hip injury. Hip injuries translate pain from the legs to the whole body through the nervous system. Physiotherapy experts administer mild exercises to restore typical ball and socket joint movement. Before beginning any physiotherapy regimen, it is imperative first to undergo a CT scan. The scan helps determine which kind of exercises will be suitable for you without causing other ligament injuries. TENS (Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) is a modern technique used by physiotherapy experts. TENS send waves of electrical pulses to your leg via small pads while blocking nerve receptors that perceive pain. The tingling sensation by the electric pulse soothes leg pain.
Conclusion
Hip replacement techniques have become minimally invasive to repair worn-out hip bones. The recovery period for hip replacement surgery may vary depending on the pre-operative condition. Hip injuries no longer have to be sources of pain and discomfort. You should schedule a visit today to a hip replacement center.